The Role of Groundwater Models in Well Project Planning
The Role of Groundwater Models in Well Project Planning:
A case study on the role of groundwater models in the Pure Water Oceanside project
The Issue
Groundwater modeling and well siting, design, and construction are not mutually exclusive. Accurate modeling can be used to help support and plan well projects and provide a better understanding of the geohydrologic conditions in an aquifer— leading to more effective well designs, and greater project success. Unfortunately, using reliable groundwater models to help design and configure well projects is an important process that is often underutilized. In fact, they are often treated as two separate projects with no relation to one another.
Case Study
The City of Oceanside (City) is responsible for providing water treatment and delivery services, and wastewater collection and treatment for the City’s domestic, commercial, and irrigation customers. To help provide more than 31 million gallons of water per day to city residents, the City operates the Robert A. Weese Direct Water Filtration Plant, Mission Basin Groundwater Purification Facility (MBGPF) for brackish groundwater treatment, and the San Luis Rey Water Reclamation Facility (SLRWRF) for wastewater treatment and recycled water production. The current desalter facility has additional capacity to develop groundwater, that can be used to further augment water supplies.
To increase water supply, and improve supply sustainability, the City began the Pure Water Oceanside project—an indirect potable reuse (IPR) project that will recharge the Mission Groundwater Basin using advanced treated recycled water from SLRWRF. The advanced treated recycled water would supplement natural recharge in the groundwater basin and be extracted by down-gradient wells to enhance the City’s potable water supply, improve supply reliability, and reduce dependence on imported water.
To implement the project and better understand conditions in the Mission Groundwater Basin, the City investigated groundwater replenishment reuse projects and completed extensive hydrogeologic investigations in 2017 and 2018.
The investigations included several steps:
- Compile and review data
- Update and calibrate the Mission Basin Groundwater Model
- Run modeling scenarios to evaluate potential recharge/extraction locations
- Based on modeling results drill exploratory boreholes and conduct lithologic sampling to better understand hydrogeologic conditions in areas of interest
- Refine and recalibrate the groundwater model based on information gained through exploratory investigations
- Use the recalibrated model to simulate recharge operations to determine project feasibility and confirm injection and extraction locations.
Based on the modeling and investigation results, the City can achieve long-term sustainable groundwater production levels by redistributing recycled water injection, and groundwater extraction wells.
Idea in Brief
Groundwater modeling allows managers to identify potential project locations and detect key areas where additional information may be required. Field investigations can then be planned to maximize hydrogeologic understanding and minimize data costs. Follow-up investigations designed for model refinement enhance the ability of groundwater models to simulate local project effects. This approach was used by the City of Oceanside when implementing the Pure Water Oceanside project, a planned aquifer recharge project using advanced treated water from the City’s wastewater treatment plant, and groundwater desalter. As a result of the approach, the City was able to effectively identify injection and production well locations, and simulate facility operations to help identify the optimal project layout and design.
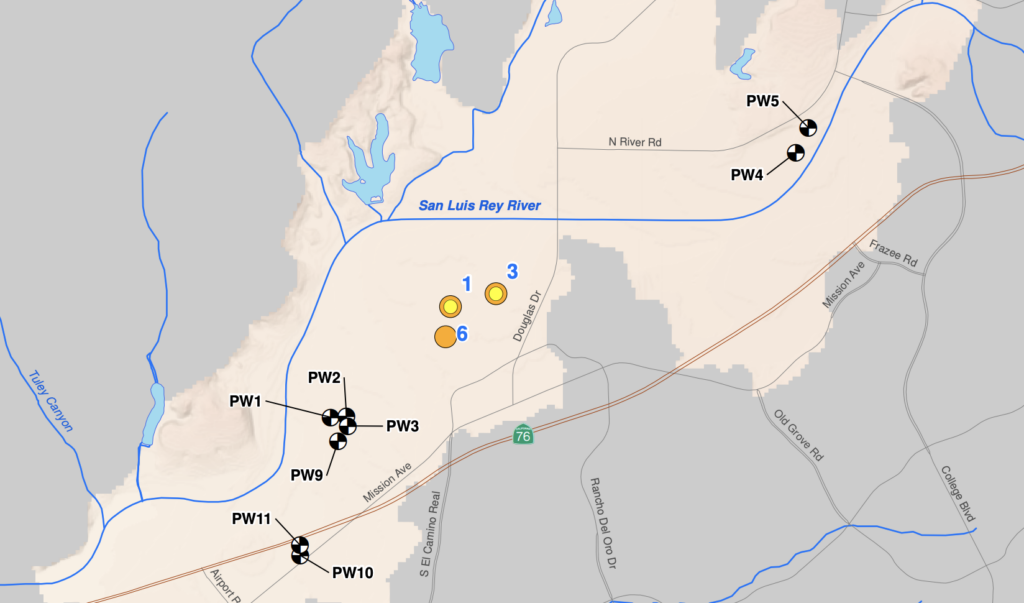
Groundwater Modeling Informed Injection Well Siting:
As illustrated above, the updated and refined groundwater model was used to run scenarios that predicted future facility operation, and helped identify optimal injection well sites to recharge the aquifer with recycled water.
Results
Currently, the City is installing both new injection and production wells in Mission Basin to help meet future demand and increase current production capacity to the existing desalter facility. The use of groundwater modeling and simulations in conjunction with field investigations provided the City with a clear path forward, enhanced insight for well siting, project design, and long-term groundwater management.
Key take-aways…
Groundwater Models can help plan future projects and forecast how those projects well affect basin management.
Groundwater modeling helps with project permitting from agencies such as the Regional Board and Division of Drinking Water.
A Groundwater Model can help move a project forward during the planning and design phases.
Discover more news
Slant Wells and Submarine Aquifers: The Future of Desalination
California’s next-generation ocean water desalination plants will get their water from submarine aquifers
Read moreLocal Company Geoscience Support Services provides slant well technology for the Monterey Peninsula Water Supply Project, saves marine life
San Dimas, CA, November 18, 2022 – Geoscience Support Services welcomes the recent approval by the California Coastal Commission of the Monterey Peninsula Water Supply Project, creating a reliable and drought-proof water supply for the Monterey Peninsula. The approval comes on the heels of the green light for the Doheny Ocean Desalination Project last month. […]
Read moreLocal Company Geoscience Support Services provides slant well technology for the Doheny Ocean Desalination Project
San Dimas, CA, October 31, 2022 – Geoscience Support Services welcomes the recent approval of the Doheny Ocean Desalination Project, creating a reliable and drought-proof water supply in South Orange County. “A key enabler of this project is the slant well design and construction method that Geoscience has developed.” says CEO Mark Williams. “Combining our […]
Read more